The CATSUS Curricular Structure is based on on-going PhD programmes with no requirement for new accreditation by the A3ES, leading to the Doctoral Degree in Chemistry or in Chemical Engineering, awarded by the granting institutions.
The CATSUS provides the specialization on Catalysis and Sustentability of the above Doctoral Degrees. The contents concern, in a flexible arrangement dependent on the student’s interests, the following fields: homogeneous, heterogeneous, supported, bio-, photo- and electro-catalyses; oil and renewable fuels; polymers; functionalized nanomaterials; supporting analytical, structural and computational methods; entrepreneurship. Although based on a settled structure, some of the core courses are newly developed and contents of others are reorganized to reflect the modern and multidisciplinary bases and applications of catalysis. Faculty and researchers from participating institutions and renowned guests (also from abroad) from academia and industry should take part in teaching with a modular structure.
The duration of the course is 4 years (including the PhD Thesis) requiring a total of 240 ECTS, distributed as follows: 30 ECTS (minimum); 60 ECTS (maximum)] and Thesis – [180 ECTS (minimum); 210 ECTS (maximum).
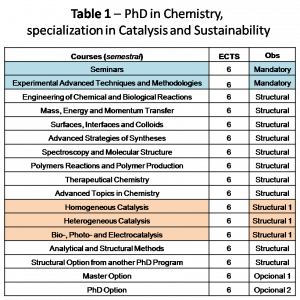
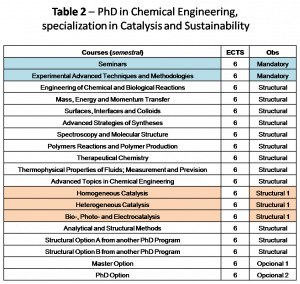
The Program is established individually by the Directive Board, taking into account the interests of the student and his/her supervisor. The overall structure (see Tables 1 and 2 for Chemistry and Chemical Engineering PhDs, respectively) is as follows:
The curricular program (1st year) matches a total of 30-60 ECTS, including:
2 MANDATORY COURSES (6 ECTS each)
- Seminars;
- Experimental Advanced Techniques and Methodologies.
2 or 3 STRUCTURAL COURSES (Type 1) (6 ECTS each)
- Homogeneous Catalysis;
- Heterogeneous Catalysis;
- Bio-, Photo- and Electrocatalysis;
1 OPTIONAL COURSE (6 ECTS): selected within the IST Master courses, or IST PhD courses (either in Chemistry, Chemical Engineering or any other PhD program).
CATSUS PhD Theses (typically, 210 ECTS) include modern themes with expertises of the team members, often with international collaborations and/or industrial links, such as:
- catalysis under environmentally benign and mild conditions towards sustainable energy processes;
- bioinspired catalysis;
- enantioselective catalysis;
- activation of small molecules with industrial, environmental or biological/pharmacological significance;
- hydrocarbon transformations;
- C-H bond activation;
- alkane functionalization;
- renewable C feedstocks;
- cross-couplings;
- synthesis of added value organic compounds;
- compounds with biological/pharmacological activity;
- functionalized materials;
- polymerization;
- catalysis by zeolites and nanostructured mesoporous catalysts;
- synthesis of zeo-like structures (SAPO’s and MeAPO’s);
- hierarchical zeolites